Photo utilities¶
Here are some utilities to manipulate picture files.
Bouding-box fitting¶
- mg.utils.photo.bbox_fitter.fit_resized(src_size, dst_size, fill, center = None)[source]¶
Gets the bounding box in the input and output image depending on source size, destination size, filling and center of interest in source image.
Parameters: - src_size – Size of input image
- dst_size – Size of output image
- fill – Whether to fill the output or pad the output image to fit the output size. Filling cuts out the parts of the image not fitting the output viewport. If not filling the viewport of the output image, borders may be added.
- center – Coords of center of interest of image. May be None for normal centering. Only used if filling is enabled.
Returns: A couple of bounding boxes in input and output images.
Sizes are of the form (width, height)
Bouding-boxes are of the form (x, y, width, height)
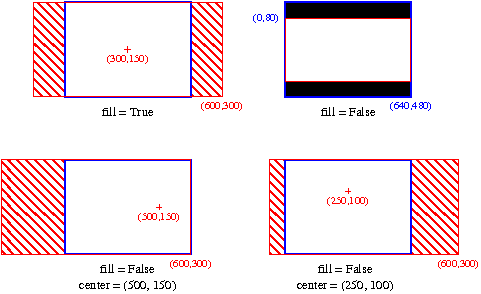
Visual representation of bounding box fitting with different modes
- red: original image size
- blue: output image size
- dashed: invisible part
- black: added borders
Example matching the figure:
>>> fit_resized((600, 300), (640, 480), True) ((100, 0, 400, 300), (0, 0, 640, 480)) >>> fit_resized((600, 300), (640, 480), False) ((0, 0, 600, 300), (0, 80, 640, 320)) >>> fit_resized((600, 300), (640, 480), True, (500, 150)) ((200, 0, 400, 300), (0, 0, 640, 480)) >>> fit_resized((600, 300), (640, 480), True, (250, 100)) ((50, 0, 400, 300), (0, 0, 640, 480))
Picture Resizing¶
Picture resizing can be used for two different jobs:
- Creating resized versions of images, for online viewing,
- Creating thumbnails, for gallery preview.
When creating resized version of images, we want the full image to be present in the resized version, and have the ratio of the input file conserved.
When creating thumbnails, tastes changes. Some prefer to have the complete scene, others prefer to have a square image with the most important part of the scene in. The Picture Resizing module makes no assumption about the kind of resizing done.
Implementation is pluggable, implementations currently exist for PIL and Evas. The first available one will be used transparently. All resizers implement the API defined in ResizerBase. As an user, you should import mg.utils.photo.resizer.resizer, which is an instance implementing ResizerBase:
from mg.utils.photo.resizer import resizer
- class mg.utils.photo.resizer.base.ResizerBase(**params)[source]¶
ResizerBase is a tool to resize images in an automated way. Whatever the parameters, aspect ratio of image wont be modified, therefore image wont be deformed.
- set_output_size(size, mode)[source]¶
Sets the output parameters
Parameters: - size – Output size
- mode – Mode of resizing, in LETTERBOX, PAN_SCAN or SCALE.
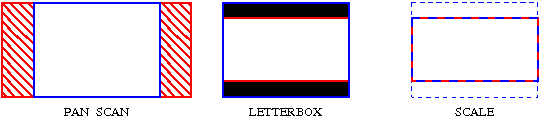
Fitting modes:
- PAN_SCAN¶
Fill the whole output image size with input image, fitting the shortest side of the image. Longest side of the input image may be partly discarded.
- LETTERBOX¶
Make the output image contain the whole input image, adding black borders if necessary
- SCALE¶
Scale input image to fit in the output bounding box. Resulting image size may be smaller than given output size.
- resize(output_filename, input_filename, center=None, rot_count=0)[source]¶
Opens the given file as source image to resize, and save its resized version according to parameters.
Parameters: - output_filename – Path to an image file to save resized version to
- input_filename – Path to an image file to open
- center – Optional coords of center of interest of image. If ommitted, image is centered normally. Only relevant for PAN_SCAN mode. See Visual representation of bounding box fitting with different modes for more information.
- rot_count – Count of 90-degree rotations to apply to image, clockwise. This transformation changes nothing to the output image aspect. Rotation is achived before fitting bounding boxes.
Example:
>>> files = ('a.jpg', 'b.jpg', 'c.jpg') >>> from mg.utils.photo.resizer import resizer >>> resizer.set_output_size(size = (120, 120), mode = resizer.PAN_SCAN) >>> for filename in files: ... resizer.resize("thumbnails/" + filename, "originals/" + filename) ... >>> resizer.set_output_size(size = (640, 480), mode = resizer.SCALE) >>> for filename in files: ... resizer.resize("view_640/" + filename, "originals/" + filename) ...